The birth of the World Wide Web
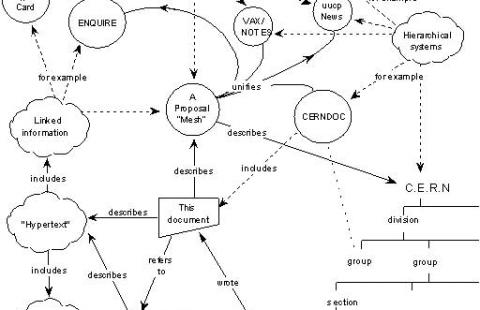
Sir Tim Berners-Lee submitted his first proposal for what became the World Wide Web
In March 1989, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, while working…
Know moreManagement proposal for a World Wide Web project
In November 1990, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, together…
Know more
The world's first browser/editor, website and server go live at CERN
By Christmas 1990, Sir Berners-Lee had defined…
Know moreSir Berners-Lee announces the WWW software on the Internet
In August 1991, Sir Berners-Lee announced his WWW…
Know moreA small but growing number of Web servers and browsers
By late 1992, the WWW project had a growing list…
Know moreCERN puts the World Wide Web in the public domain
On 30 April 1993, CERN issued a statement…
Know moreFirst International World Wide Web conference held at CERN
In May 1994, Robert Cailliau organized the world’…
Know moreTim Berners-Lee founds the World Wide Web Consortium
In October 1994, Tim Berners-Lee founded the…
Know moreMore than 10,000 Web servers around the world
By the end of 1994, the Web had 10,000 servers -…
Know more
Embed this timeline
Sir Tim Berners-Lee submitted his first proposal for what became the World Wide Web
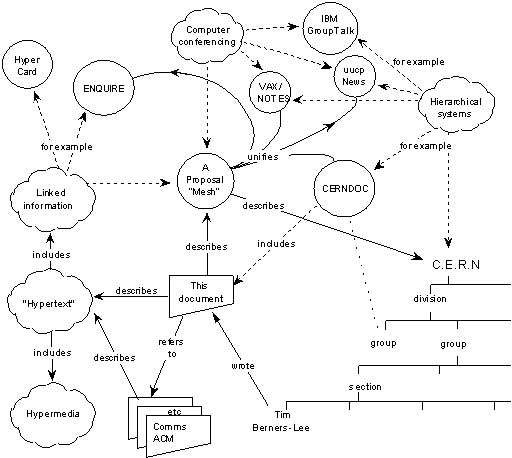
In March 1989, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, while working at CERN, wrote a proposal to develop a distributed information system. He resubmitted a slightly edited version in May 1990.
Management proposal for a World Wide Web project
In November 1990, Sir Tim Berners-Lee, together with CERN colleague, Robert Cailliau, submitted a formal management proposal for ‘WorldWideWeb: Proposal for a HyperText Project’.
The world's first browser/editor, website and server go live at CERN
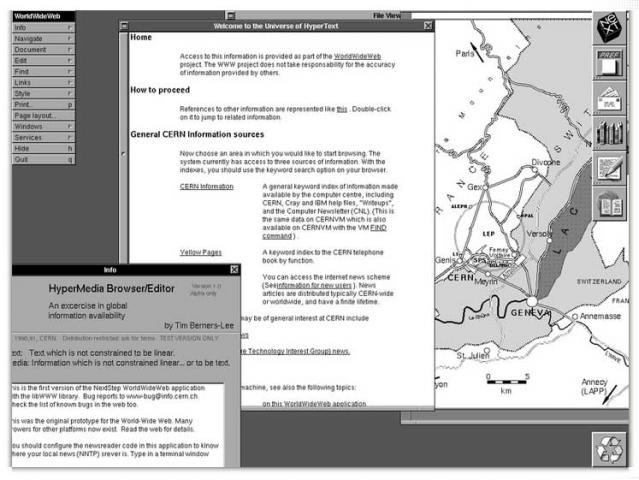
By Christmas 1990, Sir Berners-Lee had defined the Web’s basic concepts, the html, http and URL, and he had written the first browser/editor and server software. info.cern.ch was the address of the world's first web server, running on a NeXT computer at CERN. The world's first web page address provided information about the World Wide Web project.
Line Mode browser available at CERN
By March 1991, a simple ‘Line-Mode’ browser was made available to users of CERN’s central computers. Although it had less features than the more sophisticated NeXT browser/editor, it had the big advantage of being able to run on a wider range of computers. It was written by Nicola Pellow during her student work placement at CERN. A project to restore the first ever Website includes a description of the Line Mode browser.
Sir Berners-Lee announces the WWW software on the Internet
In August 1991, Sir Berners-Lee announced his WWW software on Internet newsgroups and interest in the project spread beyond the physics community. The first announcement was on 6 August 1991 to alt.hypertext, a newsgroup for hypertext enthusiasts. He described the project and provided instructions for obtaining the WWW software from CERN.
First web server outside Europe
On 12 December 1991, the first web server outside Europe was installed at the Stanford Linear Accelerator Center (SLAC) in California. It provided access to SPIRES, a database with information for scientists working in HEP (High Energy Physics), including the ability to search for publications.
WWW moves from prototype to production
By January 1992, the WWW software at CERN had matured from an early prototype to a useful and reliable service. Through CERN’s Computer Newsletter, thousands of scientists learnt how they could use the web to access a useful set of information, e.g. phone numbers, email addresses, news groups, as well as computing and software documentation.
A small but growing number of Web servers and browsers
By late 1992, the WWW project had a growing list of early web servers. They were mainly located at academic sites collaborating with CERN but interest was starting to spread beyond academia. Development was also progressing on early graphical browsers (e.g. MIDAS by Tony Johnson from SLAC, Viola by Pei Wei from technical publisher O'Reilly Books, and Erwise by Finnish students from Helsinki University of Technology).
First pre-release of the Mosaic browser
From January 1993, the National Center for Supercomputing Applications (NCSA) at the University of Illinois, provided pre-releases of its Mosaic browser for the Unix X Window System. The first official release was on 21 April 1993. Mosaic quickly gained popularity, becoming the browser of choice, with its user-friendly graphical interface and easy installation. Versions of Mosaic running on PC and Mac became available later that year.
CERN puts the World Wide Web in the public domain
On 30 April 1993, CERN issued a statement putting the Web into the public domain, ensuring that it would act as an open standard. The move had an immediate effect on the spread of the web. Further licensing actions were taken to allow the Web to evolve and flourish. By late 1993 there were over 500 known web servers, and the WWW accounted for 1% of Internet traffic.
First International World Wide Web conference held at CERN
In May 1994, Robert Cailliau organized the world’s First International World Wide Web Conference at CERN. It was attended by 380 users and developers, and was hailed as the “Woodstock of the Web”.
Tim Berners-Lee founds the World Wide Web Consortium
In October 1994, Tim Berners-Lee founded the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) – at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology laboratory for computer science – in collaboration with CERN and with support from DARPA and the European Commission. Sir Berners-Lee moved to the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), from where he remains Director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C).
More than 10,000 Web servers around the world
By the end of 1994, the Web had 10,000 servers - of which 2000 were commercial - and 10 million users. Traffic was equivalent to shipping the collected works of Shakespeare every second.
Celebrating the Web@30
In March 2019, it will be 30 years since Sir Tim Berners-Lee submitted his proposal for what would become the World Wide Web. To mark this occasion, CERN will hold an event to celebrate the Web@30. For the 29th anniversary, in March 2018, Sir Tim Berners-Lee published a letter to the world about issues facing the web today: https://webfoundation.org/2018/03/web-birthday-29/.